우선순위 큐
12 Dec 2019 | Algorithm우선순위 큐
우선순위 큐
- 우선순위 큐는 평범한 큐나 스택과 비슷한 축약 자료형이다. 그러나 각 원소들은 우선순위를 갖고 있다.
- 우선순위 큐에서 높은 우선순위를 가진 원소는 낮은 우선순위를 가진 원소보다 먼저 처리된다
-
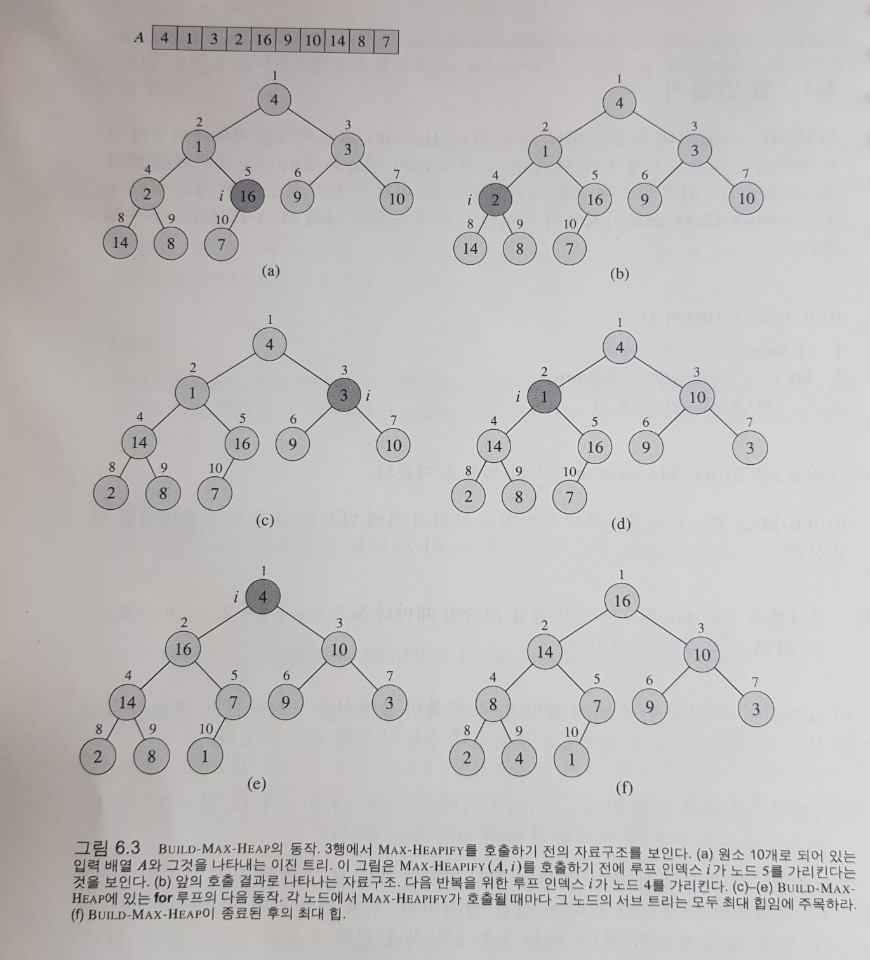
우선순위 큐는 “리스트”나 “맵”과 같이 추상적인 개념이다. 마치 리스트는 연결 리스트나 배열로 구현될 수 있는 것과 같이, 우선순위 큐는 힙이나 다양한 다른 방법을 이용해 구현될 수 있다.
-
배열, 링크드 리스트로도 구현할 수 있으나
- 배열의 경우 삽입,삭제의 비효율성
- 링크드 리스트의 경우 검색의 비효율성이 존재하고
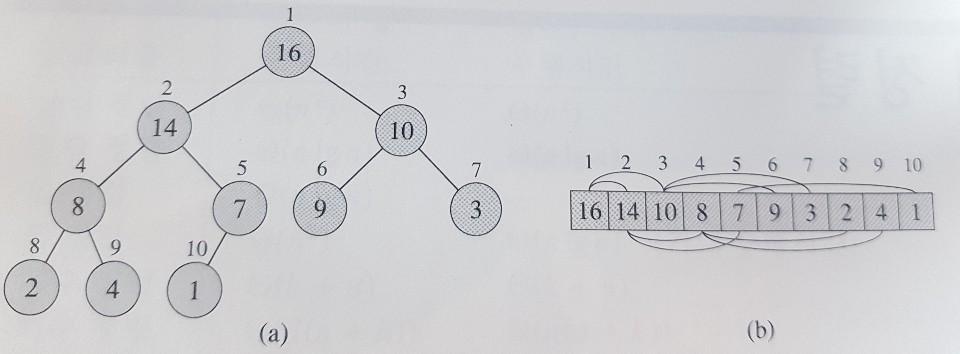
우선순위라는 최대값을 찾기에 적합한 힙(최대 힙)으로 구현한다.
- 힙 내부는 배열로 구현한다.
우선 순위 큐는 다음 연산을 제공하여야 한다
- Maximum(S)
- ExtractMax(S)
- IncreaseKey(S,i,key)
- Insert(S,key)
Maximum(S)
- 힙의 최대값을 리턴한다.
- 시간복잡도는 O(1)
//pseudocode
Maximum(S)
return S[0];
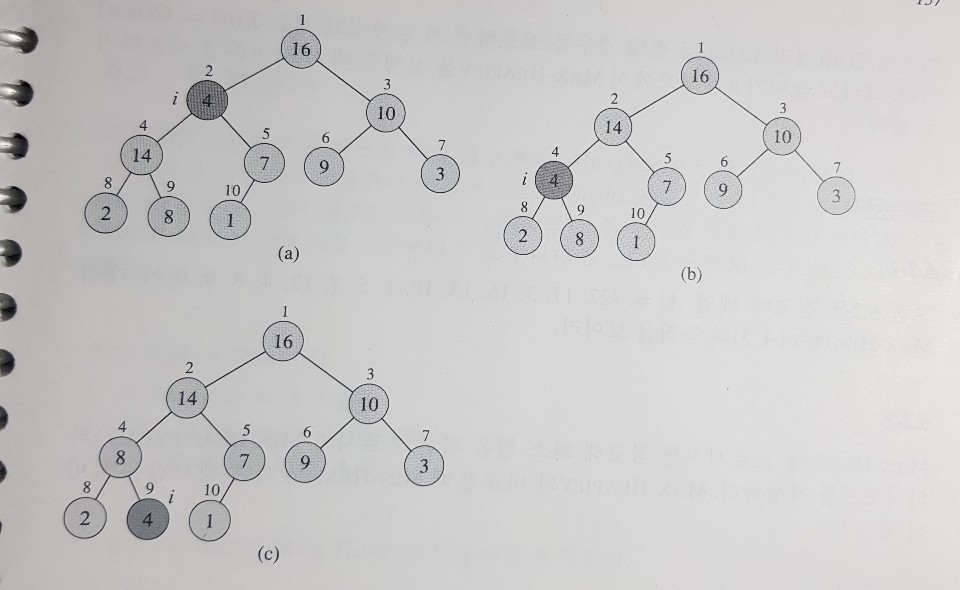
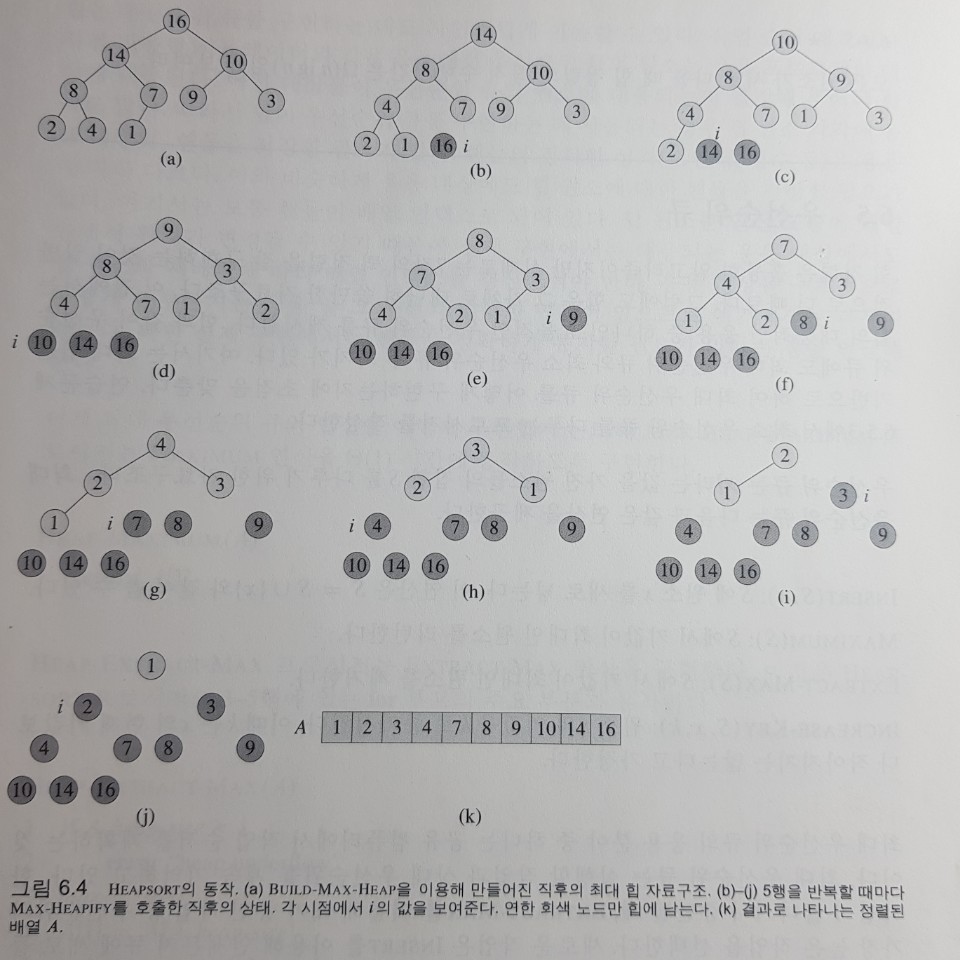
ExtractMax(S)
-
힙에서 최대값을 리턴하고 힙에서 제거한다.
-
시간복잡도는 O(1) + O(logn) (MaxHeapify) 이므로 O(logn)
//pseudocode
ExtractMax(S)
if(S.heap_size < 1)
error "heap underflow";
max = S[0];
S[0] = S[S.heap_size-1];
S.heap_size = S.heap_size -1;
MaxHeapify(S,0);
return max;
IncreaseKey(S,i,k)
-
힙 S의 인덱스 i의 키 값을 k로 증가시킨다.
-
시간복잡도는 O(1) + O(logn) 이므로 O(logn)
//pseudocode
IncreaseKey(S,i,key)
if(key < S[i])
error "새로운 키가 현재 키보다 작다";
S[i] = key;
while(i > 1 and S[Parent(i)] < S[i])
S[i] <-> S[Parent(i)];
i = Parent(i);
Insert(S,key)
-
힙에 새로운 키 값을 추가한다.
-
시간복잡도는 IncreaseKey()를 이용하므로 O(logn)
//pseudocode
Insert(S,key)
S.heap_size = S.heap_size + 1;
IncreaseKey(S,S.heap_size,key);
자바로 우선순위 큐 구현
-
자바에 존재하는 PriorityQueue를 상속받지 않고 Heap 클래스를 만들어 구현해보았다.
-
테스트 코드
class PriorityQueueTest {
private PriorityQueue priorityQueue;
private int[] input;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp(){
input = new int[]{15,13,9,5,12,8,7,4,0,6,2,1};
priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(input);
}
@Test
public void testGetMaximum() throws Exception {
assertEquals(priorityQueue.getMaximum(), 15);
}
@Test
public void testExtractMax() throws Exception {
int max = priorityQueue.extractMax();
assertEquals(max, 15);
assertEquals(priorityQueue.getMaximum(),13);
assertEquals(priorityQueue.size(),11);
}
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception {
priorityQueue.insert(30);
assertEquals(priorityQueue.getMaximum(), 30);
priorityQueue.insert(45);
assertEquals(priorityQueue.getMaximum(),45);
}
}
- 알고리즘
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* have a higher priority if value is bigger
*/
public class PriorityQueue {
private Heap heap;
public PriorityQueue(int[] src){
heap = new Heap(src);
}
public int size() {
return heap.size();
}
public int extractMax() throws Exception {
if(heap.size() < 1)
throw new Exception("heap underflow");
int max = heap.get(0);
heap.set(0,heap.get(getLastIndex()));
heap.decrementSize();
MaxHeapify(0);
return max;
}
public int getMaximum() throws Exception {
return heap.get(0);
}
private int getLastIndex(){
return heap.size()-1;
}
public void increaseKey(int idx, int key) throws Exception {
if(idx >= heap.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
if(key < heap.get(idx))
throw new Exception("new key is smaller than exist value");
heap.set(idx,key);
while(idx > 0 && heap.get(heap.getParentIndex(idx)) < heap.get(idx)){
swap(idx, heap.getParentIndex(idx));
idx = heap.getParentIndex(idx);
}
}
public void insert(int key) throws Exception {
heap.checkCapacity();
heap.incrementSize();
increaseKey(heap.size()-1, key);
}
private void MaxHeapify(int idx) {
if(idx < 0 || idx >= heap.size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
int leftIndex = heap.getLeftIndex(idx);
int rightIndex = heap.getRightIndex(idx);
int size = heap.size();
int largest = -1;
int tmp = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// compare with leftNode
if(leftIndex < size && heap.get(leftIndex) > heap.get(idx))
largest = leftIndex;
else
largest = idx;
// compare with rightNode
if(rightIndex < size && heap.get(rightIndex) > heap.get(largest))
largest = rightIndex;
// swap if parentNode is bigger than child.
if(largest != idx){
swap(idx, largest);
//reculsive call
MaxHeapify(largest);
}
}
private void swap(int from, int to) {
int tmp;
tmp = heap.get(from);
heap.set(from,heap.get(to));
heap.set(to,tmp);
}
// MaxHeap 클래스
public class Heap {
int[] array = {};
int size;
public Heap(int[] src){
array = src;
size = array.length;
}
public Heap(){
array = new int[10];
size = array.length;
}
public int getLeftIndex(int idx){
return 2*idx+1;
}
public int getRightIndex(int idx){
return 2*idx+2;
}
public int getParentIndex(int idx){return idx/2;}
// heap's size
public int size(){
return size;
}
// array's size
public int length(){
return array.length;
}
public void incrementSize(){ size++; }
public void decrementSize(){
size--;
}
public int get(int idx) {
return array[idx];
}
// if heap's size is bigger than array's length, grow array's size;
private void checkCapacity() {
int oldCapacity = length();
if(size >= oldCapacity){
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + 10;
array = Arrays.copyOf(array, newCapacity);
}
}
public int[] getHeap(){
return array;
}
public boolean isValid(int idx){
return size-1 >= idx ? true : false;
}
public void set(int idx, int value) {
if(isValid(idx)){
array[idx] = value;
return;
}
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
}
}
ref. wiki
ref. Introduction to Algorithms

 jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그
jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그