버블정렬
19 Dec 2019 | Algorithm버블정렬
버블정렬
- 두 인접한 원소를 비교하여 정렬하는 알고리즘
- 최선의 경우 시간복잡도는 O(n) : 이미 정렬되어 있는 경우
- 최악의 경우 시간복잡도는 O(n^2) : 반대로 정렬되어 있는 경우
- 추가 공간이 필요하지 않다
//pseudocode
BubbleSort(A){
for(i=1 to A.length-1){
for(j=A.length downto i+1){
if(A[j]<A[j-1])
swap(A[j],A[j-1]);
}
}
}
최악의 경우 시간복잡도가 O(n^2)인 이유는 내부 for문의 연산횟수 때문이다.
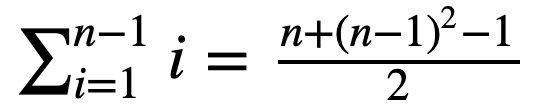
Java로 버블정렬 구현
- 테스트 코드
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.Arrays;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertArrayEquals;
class BubbleSortTest {
@Test
public void testBestTimeComplexity(){
int[] input = new int[]{1,2,3,4,5};
int[] answer = Arrays.copyOf(input,input.length);
Arrays.sort(answer);
BubbleSort.bubbleSort(input);
assertArrayEquals(input,answer);
}
@Test
public void testUnSortedArray(){
int[] input = {64,34,25,12,22,11,90};
int[] answer = Arrays.copyOf(input,input.length);
Arrays.sort(answer);
BubbleSort.bubbleSort(input);
assertArrayEquals(input,answer);
}
@Test
public void testWorstTimeComplexity(){
int[] input = {5,4,3,2,1};
int[] answer = Arrays.copyOf(input,input.length);
Arrays.sort(answer);
BubbleSort.bubbleSort(input);
assertArrayEquals(input,answer);
}
}
- 알고리즘
public class BubbleSort {
public static void bubbleSort(int[] src) {
int size = src.length;
boolean swapped;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
swapped = false;
for (int j = size - 1; j >= i; j--) {
if (compareTo(src[j], src[j - 1]) < 0) {
swap(src, j, j - 1);
swapped = true;
}
}
// 이미 정렬된 배열인 경우 정렬을 종료한다(시간복잡도: O(n))
if (swapped == false)
break;
}
}
private static void swap(int[] src, int i, int j) {
int tmp = src[i];
src[i] = src[j];
src[j] = tmp;
}
private static int compareTo(int a, int b) {
if (a > b)
return 1;
else if (a == b)
return 0;
else return -1;
}
}

 jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그
jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그