버킷정렬
18 Dec 2019 | Algorithm버킷 정렬
버킷 정렬
- 버킷정렬에서는 [0,1) 범위에서 원소를 균일하게 분포시키도록 하는 무작위 과정을 통해 입력이 균일하고 독립적으로 만들어 졌다고 가정한다.
- 평균 O(n)의 시간복잡도를 가진다.
- 정렬을 위해 추가 공간이 필요하다.
//pseudocode
BucketSort(A){
n=A.length;
//B[0..n-1]를 새로운 배열이라 하자
for(i=0 to n-1)
B[i]를 빈 리스트로 만든다.
for(i=1 to n)
A[i]를 리스트 B[nA[i]]에 삽입한다.
for(i=0 to n-1)
B[i]를 삽입 정렬을 사용해 정렬한다.(다른정렬 사용해도 된다)
리스트 B[0],B[1]...B[n-1]를 순서대로 연결한다.
}
Java로 버킷정렬 구현
- 테스트 코드
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class BucketSortTest {
private double[] input;
private double[] output;
@BeforeEach
public void setUp(){
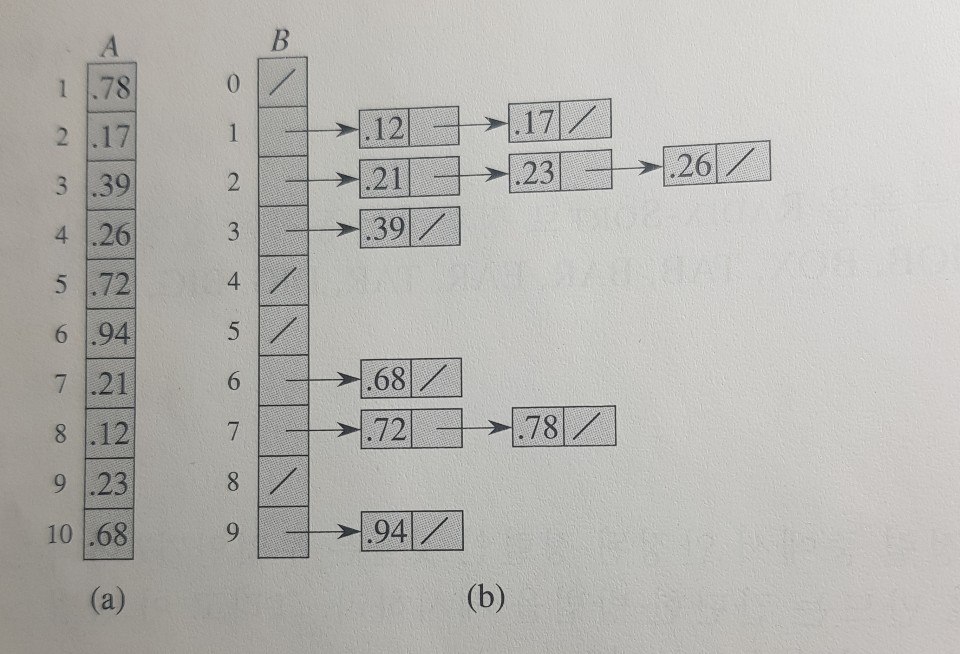
input = new double[]{0.78,0.17,0.39,0.26,0.72,0.94,0.21,0.12,0.23,0.68};
output = new double[]{0.12,0.17,0.21,0.23,0.26,0.39,0.68,0.72,0.78,0.94};
}
@Test
public void test(){
double[] result = BucketSort.sort(input);
assertArrayEquals(result,output);
}
}
- 알고리즘
import java.util.*;
public class BucketSort {
public static double[] sort(double[] src){
double[] result = new double[src.length];
int resultIdx = 0; // 버킷 별로 정렬된 원소를 result 배열에 넣을 때 필요한 idx
// [List<Double>,List<Double>,List<Double>...] 배열을 만든다(버킷)
List<Double>[] buckets = new ArrayList[10];
for(int i=0; i<src.length; i++){
int idx = (int) ((src[i]*src.length)%10);
if(buckets[idx] == null){
buckets[idx] = new ArrayList<>();
}
buckets[idx].add(src[i]);
}
for(int i=0; i<buckets.length; i++){
// 버킷별로 삽입정렬로 정렬한다
InsertionSort(buckets[i]);
List<Double> sorted = buckets[i];
if(sorted == null)
continue;
// 버킷별로 정렬한 원소를 result 배열에 담는다
for(int j=0; j<sorted.size(); j++){
result[resultIdx++] = sorted.get(j);
}
}
return result;
}
private static void InsertionSort(List<Double> src){
if(src == null)
return;
for (int i = 1; i < src.size(); i++) {
double key = src.get(i);
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && src.get(j) > key) {
src.set(j+1,src.get(j));
j--;
}
src.set(j + 1, key);
}
}
}
ref. Introduction to Algorithms

 jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그
jayyhkwon의 개발공부로그